What Is "Ozempic Face"?
“Ozempic face” is a term coined by dermatologists and aesthetic doctors to describe the facial gauntness or premature aging appearance seen in some patients who take Ozempic (semaglutide) or other GLP-1 receptor agonists like Wegovy or Mounjaro for type 2 diabetes or weight loss. These drugs can lead to rapid fat loss, including in the face, causing:
Hollow cheeks
Loose skin
Sharper jawlines
Aged appearance even in younger patients
This condition is not dangerous but can significantly affect a person’s self-image and confidence.

Why Does Ozempic Cause Facial Aging?
GLP-1 medications like Ozempic work by suppressing appetite, leading to significant fat reduction. While weight loss is often the goal, the facial fat pads—critical for a youthful look—also shrink. This sudden fat loss can lead to:
Deflation of facial volume
Skin laxity (especially if skin elasticity is already reduced due to age)
Increased visibility of fine lines and wrinkles
Patients over 40 may notice these changes more dramatically due to natural collagen decline.
Top Treatments for Ozempic Face
Managing Ozempic face involves restoring volume, tightening skin, and stimulating collagen. Below are evidence-based and FDA-cleared solutions:
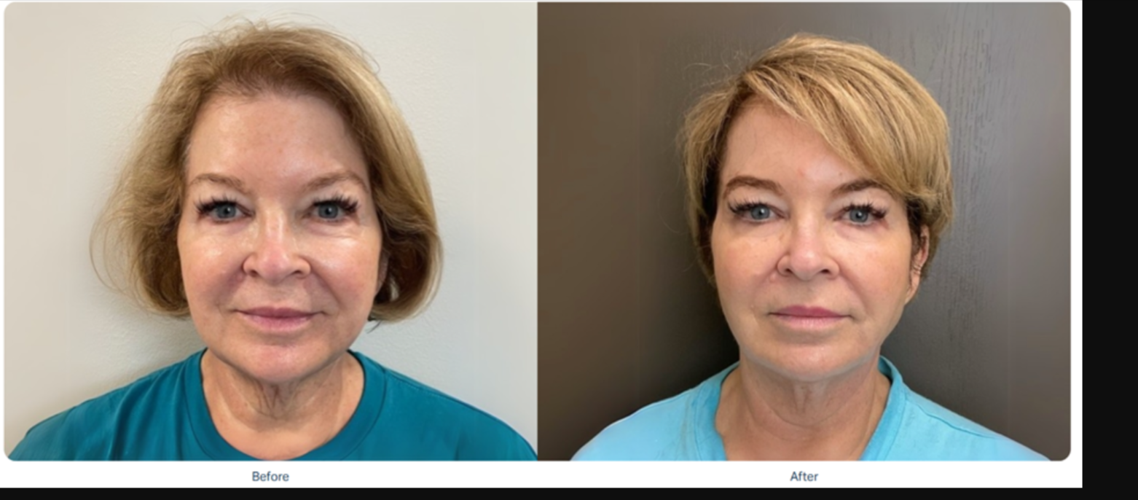
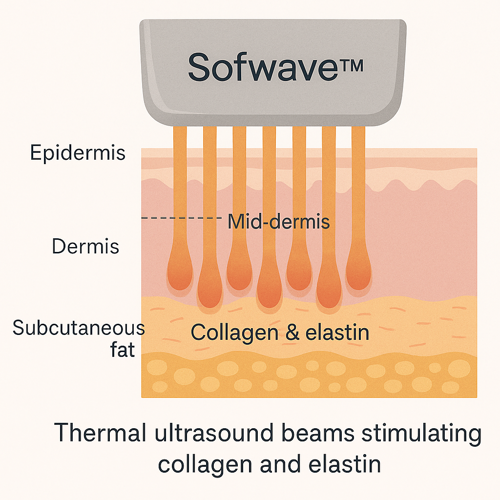
1. Ultrasound Skin Tightening – Sofwave™ Technology
One of the non-invasive leaders in treating Ozempic face is Sofwave™, an FDA-cleared technology that uses Synchronous Ultrasound Parallel Beam (SUPERB™) to:
Stimulate collagen and elastin production
Lift and tighten midface and jawline
Improve skin texture and laxity
Sofwave™ treatments require no downtime and can significantly improve facial sagging caused by fat loss.

2. Dermal Fillers (Hyaluronic Acid or Biostimulants)
Injectable fillers can help restore lost volume in the cheeks, temples, and jawline. Common options include:
Hyaluronic acid fillers (e.g., Juvederm, Restylane)
Sculptra or Radiesse (which also stimulate collagen production)
Fillers are often the first line of treatment and can be combined with ultrasound or laser treatments.
3. Radiofrequency (RF) Microneedling
Devices like Morpheus8 and Secret RF combine microneedling with radiofrequency to:
Tighten skin
Improve elasticity
Trigger collagen and elastin remodeling
They are effective for patients with skin laxity without significant volume loss.
4. Laser Skin Resurfacing (CO2 or Fractional Lasers)
If skin texture and fine lines are dominant concerns, fractional laser resurfacing can:
Stimulate new collagen
Improve tone and texture
Smooth wrinkles
It may not address deep volume loss but can complement other therapies.
5. Fat Grafting (Autologous Fat Transfer)
In more severe cases, a plastic surgeon may perform fat grafting, harvesting fat from other body parts and injecting it into the face. It offers longer-lasting results and is considered more natural.
How to Prevent or Minimize Ozempic Face?
If you are on semaglutide or a similar GLP-1 drug:
Lose weight gradually: Sudden loss accelerates facial volume decline.
Maintain hydration and collagen-rich nutrition (vitamin C, protein).
Use topical retinoids and sunscreen to protect skin integrity.
Consult a dermatologist early if signs appear.
Psychological and Aesthetic Considerations
The impact of Ozempic face isn't merely aesthetic. Many patients report:
Feeling self-conscious
Experiencing regret about weight loss outcomes
Anxiety about aging appearance
Treatment should address emotional well-being alongside aesthetic restoration.
Ozempic face is a treatable condition resulting from the unintended fat loss due to GLP-1 agonists. Thanks to non-invasive innovations like Sofwave™ and the versatility of dermal fillers, patients have effective options to restore a youthful, natural look without surgery.
References
E. Mishori, "Ozempic Face: What Is It and How to Treat It," The Washington Post, 2023.
American Society for Dermatologic Surgery, "Soft Tissue Fillers for Volume Loss."
Sofwave Medical Inc., "Understanding and Preventing Ozempic Face."
FDA, "Ultrasound and Radiofrequency Devices for Skin Tightening," fda.gov.
R. Nahas et al., "Facial Fat Loss and Restoration: Overview of Options," Aesthetic Surgery Journal, 2022.

(0) comments
We welcome your comments
Log In
Post a comment as Guest
Keep it Clean. Please avoid obscene, vulgar, lewd, racist or sexually-oriented language.
PLEASE TURN OFF YOUR CAPS LOCK.
Don't Threaten. Threats of harming another person will not be tolerated.
Be Truthful. Don't knowingly lie about anyone or anything.
Be Nice. No racism, sexism or any sort of -ism that is degrading to another person.
Be Proactive. Use the 'Report' link on each comment to let us know of abusive posts.
Share with Us. We'd love to hear eyewitness accounts, the history behind an article.